11. flox: Advanced Tools for GroupBy and Resample#
Flox is a groupby package designed for xarray and dask. In fact, the built-in groupby function in xarray is based on Flox. Using Flox allows more flexibility for grouping and aggregation, especially when working with large datasets or custom grouping logic. In this chapter, we will mainly introduce how to use xarray in flox.
The syntax of flox.xarray.xarray_reduce is as follow:
flox.xarray.xarray_reduce(obj, *by, func, expected_groups=None, isbin=False, sort=True, dim=None, fill_value=None, dtype=None, method=None, engine=None, keep_attrs=True, skipna=None, min_count=None, reindex=None, **finalize_kwargs)
We will use several examples to show how to set these options.
Example 1: Calculate the OLR climatology.
import xarray as xr
import numpy as np
from flox.xarray import xarray_reduce
olr = xr.open_dataset('./data/olr.nc').olr
olr
<xarray.DataArray 'olr' (time: 8760, lat: 90, lon: 360)> Size: 1GB
[283824000 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* time (time) datetime64[ns] 70kB 1998-01-01 1998-01-02 ... 2021-12-31
* lon (lon) float32 1kB 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 ... 356.5 357.5 358.5 359.5
* lat (lat) float32 360B -44.5 -43.5 -42.5 -41.5 ... 41.5 42.5 43.5 44.5
Attributes:
standard_name: toa_outgoing_longwave_flux
long_name: NOAA Climate Data Record of Daily Mean Upward Longwave Fl...
units: W m-2
cell_methods: time: mean area: meanolr_MonClim = xarray_reduce(olr,
olr.time.dt.month,
func='nanmean',
isbin=False,
dim='time')
olr_MonClim
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
KeyboardInterrupt Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[2], line 1
----> 1 olr_MonClim = xarray_reduce(olr,
2 olr.time.dt.month,
3 func='nanmean',
4 isbin=False,
5 dim='time')
6 olr_MonClim
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/flox/xarray.py:410, in xarray_reduce(obj, func, expected_groups, isbin, sort, dim, fill_value, dtype, method, engine, keep_attrs, skipna, min_count, reindex, *by, **finalize_kwargs)
407 output_sizes = group_sizes
408 output_sizes.update({dim.name: dim.size for dim in newdims if dim.size != 0})
--> 410 actual = xr.apply_ufunc(
411 wrapper,
412 ds_broad.drop_vars(tuple(missing_dim)).transpose(..., *grouper_dims),
413 *by_da,
414 input_core_dims=input_core_dims,
415 # for xarray's test_groupby_duplicate_coordinate_labels
416 exclude_dims=set(dim_tuple),
417 output_core_dims=[output_core_dims],
418 dask="allowed",
419 dask_gufunc_kwargs=dict(
420 output_sizes=output_sizes,
421 output_dtypes=[dtype] if dtype is not None else None,
422 ),
423 keep_attrs=keep_attrs,
424 kwargs={
425 "func": func,
426 "axis": axis,
427 "sort": sort,
428 "fill_value": fill_value,
429 "method": method,
430 "min_count": min_count,
431 "skipna": skipna,
432 "engine": engine,
433 "reindex": reindex,
434 "expected_groups": tuple(expected_groups_valid_list),
435 "isbin": isbins,
436 "finalize_kwargs": finalize_kwargs,
437 "dtype": dtype,
438 "core_dims": input_core_dims,
439 },
440 )
442 # restore non-dim coord variables without the core dimension
443 # TODO: shouldn't apply_ufunc handle this?
444 for var in set(ds_broad._coord_names) - set(ds_broad._indexes) - set(ds_broad.dims):
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/computation.py:1258, in apply_ufunc(func, input_core_dims, output_core_dims, exclude_dims, vectorize, join, dataset_join, dataset_fill_value, keep_attrs, kwargs, dask, output_dtypes, output_sizes, meta, dask_gufunc_kwargs, on_missing_core_dim, *args)
1256 # feed datasets apply_variable_ufunc through apply_dataset_vfunc
1257 elif any(is_dict_like(a) for a in args):
-> 1258 return apply_dataset_vfunc(
1259 variables_vfunc,
1260 *args,
1261 signature=signature,
1262 join=join,
1263 exclude_dims=exclude_dims,
1264 dataset_join=dataset_join,
1265 fill_value=dataset_fill_value,
1266 keep_attrs=keep_attrs,
1267 on_missing_core_dim=on_missing_core_dim,
1268 )
1269 # feed DataArray apply_variable_ufunc through apply_dataarray_vfunc
1270 elif any(isinstance(a, DataArray) for a in args):
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/computation.py:529, in apply_dataset_vfunc(func, signature, join, dataset_join, fill_value, exclude_dims, keep_attrs, on_missing_core_dim, *args)
524 list_of_coords, list_of_indexes = build_output_coords_and_indexes(
525 args, signature, exclude_dims, combine_attrs=keep_attrs
526 )
527 args = tuple(getattr(arg, "data_vars", arg) for arg in args)
--> 529 result_vars = apply_dict_of_variables_vfunc(
530 func,
531 *args,
532 signature=signature,
533 join=dataset_join,
534 fill_value=fill_value,
535 on_missing_core_dim=on_missing_core_dim,
536 )
538 out: Dataset | tuple[Dataset, ...]
539 if signature.num_outputs > 1:
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/computation.py:453, in apply_dict_of_variables_vfunc(func, signature, join, fill_value, on_missing_core_dim, *args)
451 core_dim_present = _check_core_dims(signature, variable_args, name)
452 if core_dim_present is True:
--> 453 result_vars[name] = func(*variable_args)
454 else:
455 if on_missing_core_dim == "raise":
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/computation.py:733, in apply_variable_ufunc(func, signature, exclude_dims, dask, output_dtypes, vectorize, keep_attrs, dask_gufunc_kwargs, *args)
728 broadcast_dims = tuple(
729 dim for dim in dim_sizes if dim not in signature.all_core_dims
730 )
731 output_dims = [broadcast_dims + out for out in signature.output_core_dims]
--> 733 input_data = [
734 (
735 broadcast_compat_data(arg, broadcast_dims, core_dims)
736 if isinstance(arg, Variable)
737 else arg
738 )
739 for arg, core_dims in zip(args, signature.input_core_dims, strict=True)
740 ]
742 if any(is_chunked_array(array) for array in input_data):
743 if dask == "forbidden":
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/computation.py:735, in <listcomp>(.0)
728 broadcast_dims = tuple(
729 dim for dim in dim_sizes if dim not in signature.all_core_dims
730 )
731 output_dims = [broadcast_dims + out for out in signature.output_core_dims]
733 input_data = [
734 (
--> 735 broadcast_compat_data(arg, broadcast_dims, core_dims)
736 if isinstance(arg, Variable)
737 else arg
738 )
739 for arg, core_dims in zip(args, signature.input_core_dims, strict=True)
740 ]
742 if any(is_chunked_array(array) for array in input_data):
743 if dask == "forbidden":
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/computation.py:656, in broadcast_compat_data(variable, broadcast_dims, core_dims)
651 def broadcast_compat_data(
652 variable: Variable,
653 broadcast_dims: tuple[Hashable, ...],
654 core_dims: tuple[Hashable, ...],
655 ) -> Any:
--> 656 data = variable.data
658 old_dims = variable.dims
659 new_dims = broadcast_dims + core_dims
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/variable.py:415, in Variable.data(self)
413 return self._data
414 elif isinstance(self._data, indexing.ExplicitlyIndexed):
--> 415 return self._data.get_duck_array()
416 else:
417 return self.values
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/indexing.py:734, in LazilyVectorizedIndexedArray.get_duck_array(self)
729 # self.array[self.key] is now a numpy array when
730 # self.array is a BackendArray subclass
731 # and self.key is BasicIndexer((slice(None, None, None),))
732 # so we need the explicit check for ExplicitlyIndexed
733 if isinstance(array, ExplicitlyIndexed):
--> 734 array = array.get_duck_array()
735 return _wrap_numpy_scalars(array)
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/coding/variables.py:81, in _ElementwiseFunctionArray.get_duck_array(self)
80 def get_duck_array(self):
---> 81 return self.func(self.array.get_duck_array())
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/indexing.py:728, in LazilyVectorizedIndexedArray.get_duck_array(self)
724 array = apply_indexer(self.array, self.key)
725 else:
726 # If the array is not an ExplicitlyIndexedNDArrayMixin,
727 # it may wrap a BackendArray so use its __getitem__
--> 728 array = self.array[self.key]
729 # self.array[self.key] is now a numpy array when
730 # self.array is a BackendArray subclass
731 # and self.key is BasicIndexer((slice(None, None, None),))
732 # so we need the explicit check for ExplicitlyIndexed
733 if isinstance(array, ExplicitlyIndexed):
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/backends/netCDF4_.py:103, in NetCDF4ArrayWrapper.__getitem__(self, key)
102 def __getitem__(self, key):
--> 103 return indexing.explicit_indexing_adapter(
104 key, self.shape, indexing.IndexingSupport.OUTER, self._getitem
105 )
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/indexing.py:1012, in explicit_indexing_adapter(key, shape, indexing_support, raw_indexing_method)
985 def explicit_indexing_adapter(
986 key: ExplicitIndexer,
987 shape: _Shape,
988 indexing_support: IndexingSupport,
989 raw_indexing_method: Callable[..., Any],
990 ) -> Any:
991 """Support explicit indexing by delegating to a raw indexing method.
992
993 Outer and/or vectorized indexers are supported by indexing a second time
(...)
1010 Indexing result, in the form of a duck numpy-array.
1011 """
-> 1012 raw_key, numpy_indices = decompose_indexer(key, shape, indexing_support)
1013 result = raw_indexing_method(raw_key.tuple)
1014 if numpy_indices.tuple:
1015 # index the loaded np.ndarray
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/indexing.py:1045, in decompose_indexer(indexer, shape, indexing_support)
1041 def decompose_indexer(
1042 indexer: ExplicitIndexer, shape: _Shape, indexing_support: IndexingSupport
1043 ) -> tuple[ExplicitIndexer, ExplicitIndexer]:
1044 if isinstance(indexer, VectorizedIndexer):
-> 1045 return _decompose_vectorized_indexer(indexer, shape, indexing_support)
1046 if isinstance(indexer, BasicIndexer | OuterIndexer):
1047 return _decompose_outer_indexer(indexer, shape, indexing_support)
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/indexing.py:1142, in _decompose_vectorized_indexer(indexer, shape, indexing_support)
1138 np_indexer_elems.append(np_slice)
1139 else:
1140 # If it is a (multidimensional) np.ndarray, just pickup the used
1141 # keys without duplication and store them as a 1d-np.ndarray.
-> 1142 oind, vind = np.unique(k, return_inverse=True)
1143 backend_indexer_elems.append(oind)
1144 np_indexer_elems.append(vind.reshape(*k.shape))
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/numpy/lib/_arraysetops_impl.py:291, in unique(ar, return_index, return_inverse, return_counts, axis, equal_nan)
289 ar = np.asanyarray(ar)
290 if axis is None:
--> 291 ret = _unique1d(ar, return_index, return_inverse, return_counts,
292 equal_nan=equal_nan, inverse_shape=ar.shape, axis=None)
293 return _unpack_tuple(ret)
295 # axis was specified and not None
File /data/wtsai/micromamba/p3t/lib/python3.10/site-packages/numpy/lib/_arraysetops_impl.py:377, in _unique1d(ar, return_index, return_inverse, return_counts, equal_nan, inverse_shape, axis)
374 mask[1:] = aux[1:] != aux[:-1]
376 ret = (aux[mask],)
--> 377 if return_index:
378 ret += (perm[mask],)
379 if return_inverse:
KeyboardInterrupt:
olr: TheDataArrayvariable for which we want to calculate the climatology.olr.time.dt.month: Specifies how to group the data. Flox will group all values with the same month together.func='nanmean': The statistical function applied to each group. Flox supports many functions, including:
“all”, “any”, “count”, “sum”, “nansum”, “mean”, “nanmean”,
“max”, “nanmax”, “min”, “nanmin”, “argmax”, “nanargmax”,
“argmin”, “nanargmin”, “quantile”, “nanquantile”,
“median”, “nanmedian”, “mode”, “nanmode”,
“first”, “nanfirst”, “last”, “nanlast”isbin: Determines whether to group values by predefined bins (expected_groups). In this example, we simply group by the natural values in the data (i.e., 12 months). Usage ofisbinwill be shown in later examples.dim='time': Specifies the dimension along which to perform the aggregation (here, thetimedimension).
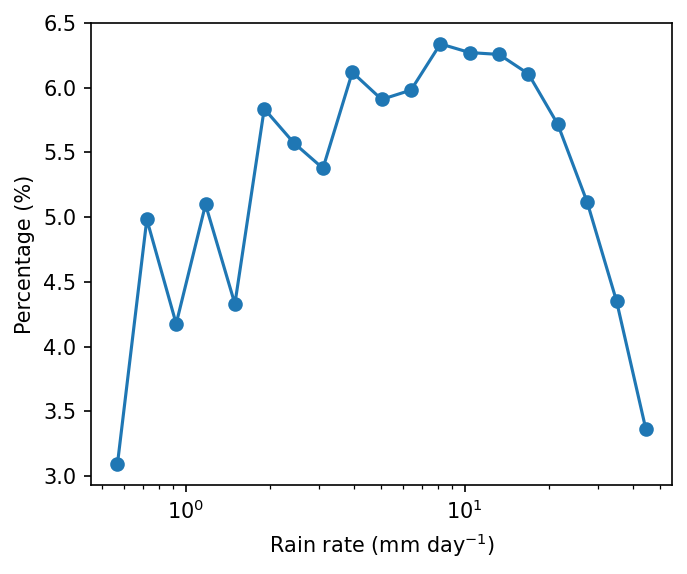
Example 2: 1-D probability distribution. Plot the probability distribution of daily precipitation rate.
Step 1: Read data.
pcp = xr.open_dataarray('./data/cmorph_sample.nc').sel(lat=slice(-15,15),lon=slice(90,160))
pcp_djf = pcp.sel(time=pcp.time.dt.month.isin([12,1,2]))
pcp_djf
<xarray.DataArray 'cmorph' (time: 2166, lat: 120, lon: 280)> Size: 291MB
[72777600 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates:
* time (time) datetime64[ns] 17kB 1998-01-01 1998-01-02 ... 2021-12-31
* lon (lon) float32 1kB 90.12 90.38 90.62 90.88 ... 159.4 159.6 159.9
* lat (lat) float32 480B -14.88 -14.62 -14.38 ... 14.38 14.62 14.88
Attributes:
standard_name: lwe_precipitation_rate
long_name: precipitation
units: mm/day
ver_note: 1998-2020: V1,0; 2021: V0.x.
comment: !!! CMORPH estimate is rainrate !!!Step 2: Count number of occurrence for each precipitation bin with flox. Technically, the precipitation is grouped by precipitation.
pdf = xarray_reduce(pcp_djf,
pcp_djf,
func='count',
isbin=True,
expected_groups=np.geomspace(0.5, 50, 20),
dim=['time','lat','lon'])
pdf_percent = pdf / pdf.sum() * 100.
pdf_percent
<xarray.DataArray 'cmorph' (cmorph_bins: 19)> Size: 152B
array([3.09464685, 4.98283472, 4.17693794, 5.09792383, 4.33013187,
5.83681144, 5.57525959, 5.37691207, 6.11883881, 5.90911831,
5.98125898, 6.33805064, 6.27095539, 6.25657 , 6.10623415,
5.71656116, 5.11653848, 4.35264337, 3.36177241])
Coordinates:
* cmorph_bins (cmorph_bins) object 152B (0.5, 0.6371374928515668] ... (39....pcp_djfis the variable being grouped — we want to group precipitation valuesbyrain rate (the secondpcp_djf).func='count': Counts how many values fall into each bin (i.e., frequency of rainfall in each intensity range).isbin=True: Indicates that we want to group precipitation values into bins, not by exact values.expected_groups=np.geomspace(0.1, 50, 20): Defines the bin edges. Here we use logarithmic spacing (geomspace) from 0.1 mm to 50 mm, divided into 20 bins, because precipitation distribution is usually logarithmic scale.dim=['time','lat','lon']: Aggregates over all dimensions (time and space), so the result is a 1D histogram of rainfall intensity.
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
mpl.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 150
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5,4))
lineplt = pdf_percent.plot.line(x='cmorph_bins', marker='o', xscale='log',ax=ax)
ax.set_ylabel('Percentage (%)')
ax.set_xlabel(r'Rain rate (mm day$^{-1}$)')
Text(0.5, 0, 'Rain rate (mm day$^{-1}$)')
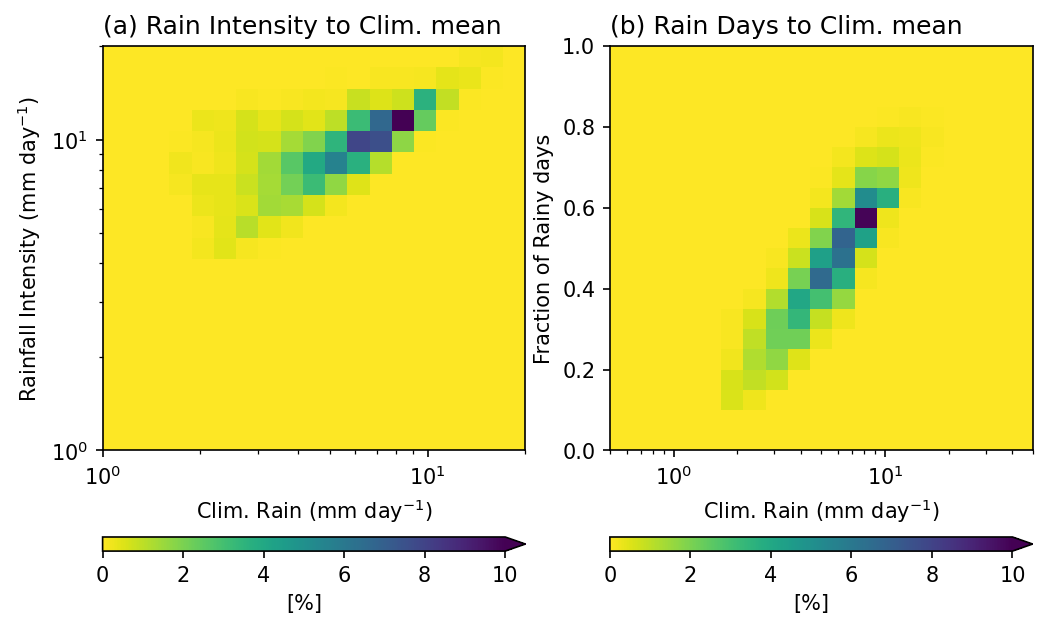
Example 3: 2-D Probability Distribution. Plot the 2-D probability distribution of annual mean rainfall, rainfall intensity, and fraction of rainy days (> 0.5 mm day \(^{-1}\) ).
These three metrics complement each other and provide a more complete picture of rainfall characteristics:
Annual mean rainfall (amount): the total rainfall, but it does not reveal whether it comes from frequent light rain or infrequent heavy rain.
Rainy days (frequency): shows how often it rains. High rainfall can result from many rainy days or from a few very wet days.
Rainfall intensity (amount per rainy day): distinguishes between light and heavy rain events.
Looking at these three variables together helps us understand how the total rainfall is distributed. This is important for interpreting climate regimes and hydrological impacts.
pcp_AnnualClm = pcp.mean(axis=0).rename('Annual_mean')
pcp_intensity = xr.where(pcp==0, np.nan, pcp).mean(axis=0,skipna=True).rename('Intensity')
# Discard no precipitation points before averaing.
pcp_days = xr.where(pcp>0.5, 1, 0).mean(axis=0,skipna=True).rename('Rain_days')
# Fraction of rainy days (> 0.5 mm day-1)
RI_Clm_pdf = xarray_reduce(pcp_intensity,
pcp_intensity,pcp_AnnualClm,
func='count',
dim=['lat','lon'],
isbin=(True,True),
expected_groups=(np.geomspace(1, 20, 20), np.geomspace(1, 20, 20)))
Days_Clm_pdf = xarray_reduce(pcp_days,
pcp_days,pcp_AnnualClm,
func='count',
dim=['lat','lon'],
isbin=(True,True),
expected_groups=(np.arange(0,1.05,0.05), np.geomspace(0.5, 50, 20)))
pcp_intensity(first argument): the variable passed to be reduced.pcp_intensity,pcp_AnnualClm: the two variables used for grouping. Flox will jointly bin data points according to rainfall intensity and annual mean rainfall.func='count': counts how many grid cells fall into each (intensity, annual rainfall) bin.dim=['lat','lon']: aggregation is applied over space to shape a histogram.isbin=(True,True): indicates both grouping variables are treated as binned quantities. The bins are based onexpected_groups: specifies the bin edges. Here both variables use log-spaced bins from 1 to 20 mm/day, which gives higher resolution at smaller values where rainfall tends to vary more strongly.
Note
The first argument pcp_intensity in this example, since func='count', is not used for its actual values**. It only provides shape and alignment for flox.
However, if the purpose is to calculate a statistic of another variable x conditioned on rainfall intensity and annual mean bins, then the first argument determines which variable is being aggregated. In that case, its values become meaningful for the computation.
Result:
RI_Clm_pdf is a 2D histogram showing how often certain combinations of rainfall intensity and annual mean rainfall occur across the spatial domain. This can be normalized to a probability distribution by dividing by the total count.
RI_Clm_pdf_percent = RI_Clm_pdf / RI_Clm_pdf.sum() * 100.
Days_Clm_pdf_percent = Days_Clm_pdf / Days_Clm_pdf.sum() * 100.
mpl.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 150
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(8,5))
ax = axes.flatten()
RI_Clm_plt = RI_Clm_pdf_percent.plot.pcolormesh(x='Annual_mean_bins',y='Intensity_bins',
xscale='log',yscale='log',
cmap='viridis_r',ax=ax[0],
vmin=0, vmax=10,
extend='max',
cbar_kwargs={'orientation': 'horizontal', 'aspect': 30, 'label': r'[%]'})
ax[0].set_title('(a) Rain Intensity to Clim. mean',loc='left')
ax[0].set_ylabel(r'Rainfall Intensity (mm day$^{-1}$)')
ax[0].set_xlabel(r'Clim. Rain (mm day$^{-1}$)')
Day_Clm_plt = Days_Clm_pdf_percent.plot.pcolormesh(x='Annual_mean_bins',y='Rain_days_bins',
xscale='log',
cmap='viridis_r',ax=ax[1],
vmin=0, vmax=10,
extend='max',
cbar_kwargs={'orientation': 'horizontal', 'aspect': 30, 'label': r'[%]'})
ax[1].set_title('(b) Rain Days to Clim. mean',loc='left')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Fraction of Rainy days')
ax[1].set_xlabel(r'Clim. Rain (mm day$^{-1}$)')
Text(0.5, 0, 'Clim. Rain (mm day$^{-1}$)')
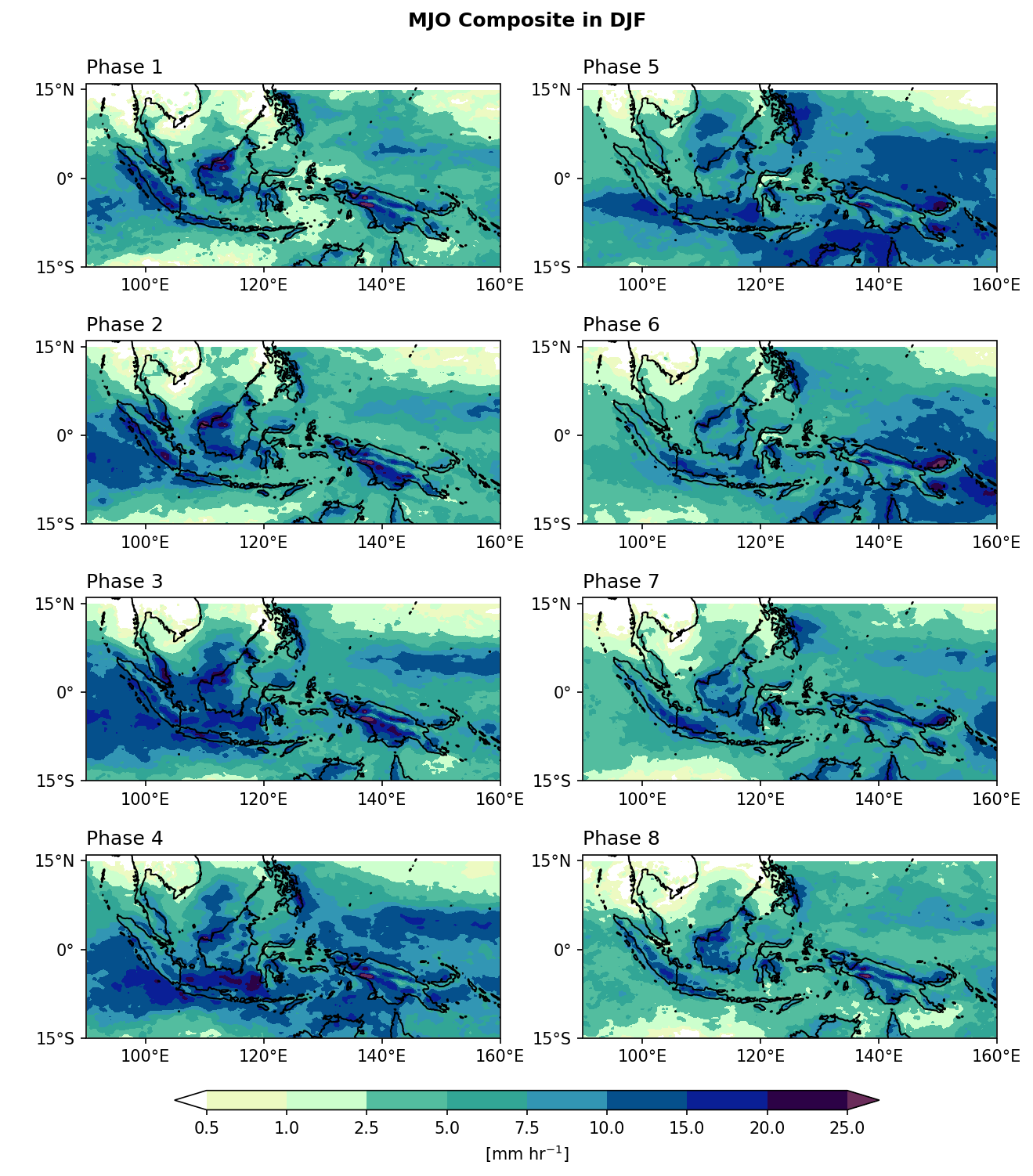
Example 4: Composite Mean. Plot rainfall composite mean for each MJO phase.
Step 1: Read MJO phase data from IRI data library.
import pandas as pd
# Read MJO data
mjo_ds = xr.open_dataset('http://iridl.ldeo.columbia.edu/SOURCES/.BoM/.MJO/.RMM/dods',
decode_times=False)
T = mjo_ds.T.values
mjo_ds['T'] = pd.date_range("1974-06-01", periods=len(T)) # Data starts from 1974-06-01
mjo_sig_phase = xr.where(mjo_ds.amplitude>=1, mjo_ds.phase, 0).rename('mjo_phase')
# Only significant (amplitude >= 1) MJO events are preserved.
mjo_slice = mjo_sig_phase.sel(T=slice("1998-01-01","2021-12-31"))
mjo_djf = mjo_slice.sel(T=mjo_slice['T'].dt.month.isin([12, 1, 2])).rename({'T':'time'})
syntax error, unexpected WORD_WORD, expecting ';' or ','
context: Attributes { T { String calendar "standard"; Int32 expires 1755820800; String standard_name "time"; Float32 pointwidth 1.0; Int32 gridtype 0; String units "julian_day"; } amplitude { Int32 expires 1755820800; String units "unitless"; Float32 missing_value 9.99999962E35; } phase { Int32 expires 1755820800; String units "unitless"; Float32 missing_value 999.0; } RMM1 { Int32 expires 1755820800; String units "unitless"; Float32 missing_value 9.99999962E35; } RMM2 { Int32 expires 1755820800; String units "unitless"; Float32 missing_value 9.99999962E35; }NC_GLOBAL { String references "Wheeler_Hendon2004"; Int32 expires 1755820800; URL Wheeler and Hendon^ (2004) Monthly Weather Review article "http://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/abs/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132%3C1917:AARMMI%3E2.0.CO;2"; String description "Real-time Multivariate MJO Index (with components of interannual variability removed)"; URL summary from BoM "http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/mjo/"; URL data source "http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/mjo/graphics/rmm.74toRealtime.txt"; String Conventions "IRIDL";}}
Illegal attribute
context: Attributes { T { String calendar "standard"; Int32 expires 1755820800; String standard_name "time"; Float32 pointwidth 1.0; Int32 gridtype 0; String units "julian_day"; } amplitude { Int32 expires 1755820800; String units "unitless"; Float32 missing_value 9.99999962E35; } phase { Int32 expires 1755820800; String units "unitless"; Float32 missing_value 999.0; } RMM1 { Int32 expires 1755820800; String units "unitless"; Float32 missing_value 9.99999962E35; } RMM2 { Int32 expires 1755820800; String units "unitless"; Float32 missing_value 9.99999962E35; }NC_GLOBAL { String references "Wheeler_Hendon2004"; Int32 expires 1755820800; URL Wheeler and Hendon^ (2004) Monthly Weather Review article "http://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/abs/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132%3C1917:AARMMI%3E2.0.CO;2"; String description "Real-time Multivariate MJO Index (with components of interannual variability removed)"; URL summary from BoM "http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/mjo/"; URL data source "http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/mjo/graphics/rmm.74toRealtime.txt"; String Conventions "IRIDL";}}
Step 2: Group the precipitation data based on the MJO phase.
mjo_phase_comp = xarray_reduce(pcp_djf,
mjo_djf,
func='nanmean',
dim='time',
isbin=False,
)
mjo_phase_comp
<xarray.DataArray 'cmorph' (mjo_phase: 9, lat: 120, lon: 280)> Size: 1MB
array([[[1.5509361 , 1.5476524 , 1.5360179 , ..., 6.1897774 ,
6.044517 , 5.838945 ],
[1.644101 , 1.5174888 , 1.6073403 , ..., 6.6764784 ,
6.6883655 , 6.3710103 ],
[1.7099406 , 1.5615454 , 1.6053046 , ..., 7.1074147 ,
7.0514264 , 6.989376 ],
...,
[1.2247697 , 1.2321248 , 1.0660772 , ..., 0.9790045 ,
0.91200596, 0.8479941 ],
[0.9963893 , 0.90916795, 0.7632095 , ..., 1.0414264 ,
0.996211 , 0.9376969 ],
[0.74106985, 0.6703715 , 0.6609807 , ..., 1.0852897 ,
1.0059881 , 0.92294204]],
[[2.1850576 , 2.1586208 , 2.3988507 , ..., 5.4770117 ,
4.7149425 , 4.7413793 ],
[2.2839081 , 2.4195402 , 2.4873564 , ..., 5.5850577 ,
4.9080462 , 5.1747127 ],
[2.4034483 , 3.0367815 , 3.254023 , ..., 5.462069 ,
5.521839 , 5.8977013 ],
...
[0.2897544 , 0.26273686, 0.29249123, ..., 0.74992985,
0.7251579 , 0.681193 ],
[0.24196492, 0.19701755, 0.1731579 , ..., 0.7130176 ,
0.6249825 , 0.6207018 ],
[0.16712281, 0.14017543, 0.15249123, ..., 0.62736845,
0.57480705, 0.5857895 ]],
[[1.9496454 , 1.8248227 , 1.8163121 , ..., 4.546099 ,
4.824823 , 5.4425535 ],
[1.9907802 , 2.1276596 , 2.283688 , ..., 4.7184396 ,
5.012766 , 5.05461 ],
[2.555319 , 2.703546 , 2.8758867 , ..., 5.4425535 ,
5.6014185 , 5.35461 ],
...,
[0.75886524, 0.72269505, 0.57588655, ..., 3.2198582 ,
3.0680852 , 3.1226952 ],
[0.8056738 , 0.6815603 , 0.55602837, ..., 3.7794328 ,
3.487234 , 3.0744681 ],
[0.5156028 , 0.56950355, 0.5382979 , ..., 3.7475178 ,
3.7709222 , 3.3829787 ]]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates:
* lon (lon) float32 1kB 90.12 90.38 90.62 90.88 ... 159.4 159.6 159.9
* lat (lat) float32 480B -14.88 -14.62 -14.38 ... 14.38 14.62 14.88
* mjo_phase (mjo_phase) float32 36B 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0
Attributes:
standard_name: lwe_precipitation_rate
long_name: precipitation
units: mm/day
ver_note: 1998-2020: V1,0; 2021: V0.x.
comment: !!! CMORPH estimate is rainrate !!!In this example, precipitation data
pcp_djfis grouped by each MJO phasemjo_djf. For each MJO phase group,func='nanmean'calculates the mean precipitation over time dimension (dim='time'). That is, all time steps belonging to the same MJO phase are averaged together.isbin=False: Means we are grouping by the exact values ofmjo_djf(the phase categories 1–8), not by bins.
Step 3: Plotting.
import cmaps
from cartopy import crs as ccrs
from cartopy.mpl.gridliner import LONGITUDE_FORMATTER, LATITUDE_FORMATTER
mpl.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 150
fig, axes = plt.subplots(4,2,
subplot_kw={'projection': ccrs.PlateCarree()},
figsize=(10,11))
ax = axes.flatten()
lon_formatter = LONGITUDE_FORMATTER
lat_formatter = LATITUDE_FORMATTER
clevs = [0.5,1,2.5,5,7.5,10,15,20,25]
porder = [0,2,4,6,1,3,5,7]
for i in range(1,9):
cf = (mjo_phase_comp[i,:,:].plot.contourf(x='lon',y='lat', ax=ax[porder[i-1]],
levels=clevs,
add_colorbar=False,
cmap=cmaps.precip_11lev,
extend='both',
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree()))
ax[porder[i-1]].coastlines()
ax[porder[i-1]].set_extent([90,160,-15,16],crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax[porder[i-1]].set_xticks(np.arange(100,180,20), crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax[porder[i-1]].set_yticks(np.arange(-15,30,15), crs=ccrs.PlateCarree()) # 設定x, y座標的範圍,以及多少經緯度繪製刻度。
ax[porder[i-1]].xaxis.set_major_formatter(lon_formatter)
ax[porder[i-1]].yaxis.set_major_formatter(lat_formatter)
ax[porder[i-1]].set_xlabel(' ')
ax[porder[i-1]].set_ylabel(' ')
ax[porder[i-1]].set_title(' ')
ax[porder[i-1]].set_title('Phase '+str(i), loc='left')
# Add a colorbar axis at the bottom of the graph
cbar_ax = fig.add_axes([0.2, 0.07, 0.6, 0.015])
# Draw the colorbar 將colorbar畫在cbar_ax這個軸上。
cbar = fig.colorbar(cf, cax=cbar_ax,
orientation='horizontal',
ticks=clevs,
label=r'[mm hr$^{-1}$]')
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.15)
plt.suptitle('MJO Composite in DJF',y=0.92,size='large',weight='bold')
plt.show()