Spectral Analysis#
We will demonstrate how to use Python to calculate power spectrum as documented in NCL website. The code is generated by Google Gemini.
First, build the pre-defined functions as follows:
import xarray as xr
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import signal
from scipy.stats import chi2
def specx_anal(data, d, sm, pct):
"""
Python version of the NCL specx_anal function.
Computes a smoothed one-dimensional power spectrum.
Parameters:
- data: Input one-dimensional time series (numpy array)
- d: Detrend option (0: subtract mean, 1: linear detrend)
- sm: Smoothing window size (odd number)
- pct: Tapering percentage at both ends of the data
Returns:
- spec_info: A dictionary containing the spectral analysis results
"""
n = len(data)
# Linear detrend
detrend_type = 'constant' if d == 0 else 'linear'
# Tapering
window = signal.windows.tukey(n, alpha=2*pct)
# Calculate Periodogram
# fs=1: sampling frequency is once per time unit (SOI for example, once per month.)
# scaling='density' obtains Power Spectral Density (PSD)
# This step integrates windowing, detrending, FFT, and computing the one-sided spectrum
freqs, pxx_raw = signal.periodogram(
data, fs=1, window=window, detrend=detrend_type, scaling='density'
)
# Smooth the spectrum: use convolution for moving average
smoother = np.ones(sm) / sm
pxx_smooth = np.convolve(pxx_raw, smoother, mode='same')
# Calculate Degrees of Freedom and bandwidth. Please refer to NCL documentation.
dof = 2 * sm
bw = dof / n # 假設 dt=1
spec_info = {
'spcx': pxx_smooth,
'frq': freqs,
'dof': dof,
'bw': bw
}
return spec_info
def specx_ci(original_data, spec_info, clevel_lower, clevel_upper):
"""
Python version of the NCL specx_ci function.
Computes confidence intervals based on red noise (AR1 process).
Returns:
- splt: A (4, n_freqs) array containing:
[0]: Smoothed data spectrum
[1]: Theoretical red noise spectrum
[2]: Lower bound of the red noise confidence interval
[3]: Upper bound of the red noise confidence interval
"""
# Extract required variables from spec_info dictionary
spcx = spec_info['spcx']
freqs = spec_info['frq']
dof = spec_info['dof']
n_freqs = len(freqs)
# Use original data to calculate lag-1 autocorrelation coefficient (r1)
mean_data = original_data.mean()
anom_data = original_data - mean_data
r1 = np.corrcoef(anom_data[:-1], anom_data[1:])[0, 1]
# Calculate theoretical red noise spectrum using the formula from Gilman et al. (1963)
red_noise_spec = (1 - r1**2) / (1 - 2 * r1 * np.cos(2 * np.pi * freqs) + r1**2)
# Normalize the total variance of the red noise spectrum to match the data spectrum
red_noise_spec_normalized = red_noise_spec * (np.sum(spcx) / np.sum(red_noise_spec))
# Calculate confidence intervals based on Chi-squared distribution
chi2_lower = chi2.ppf(clevel_lower, dof)
chi2_upper = chi2.ppf(clevel_upper, dof)
lower_bound = red_noise_spec_normalized * (chi2_lower / dof)
upper_bound = red_noise_spec_normalized * (chi2_upper / dof)
# Return results
splt = np.vstack([spcx, red_noise_spec_normalized, lower_bound, upper_bound])
return splt
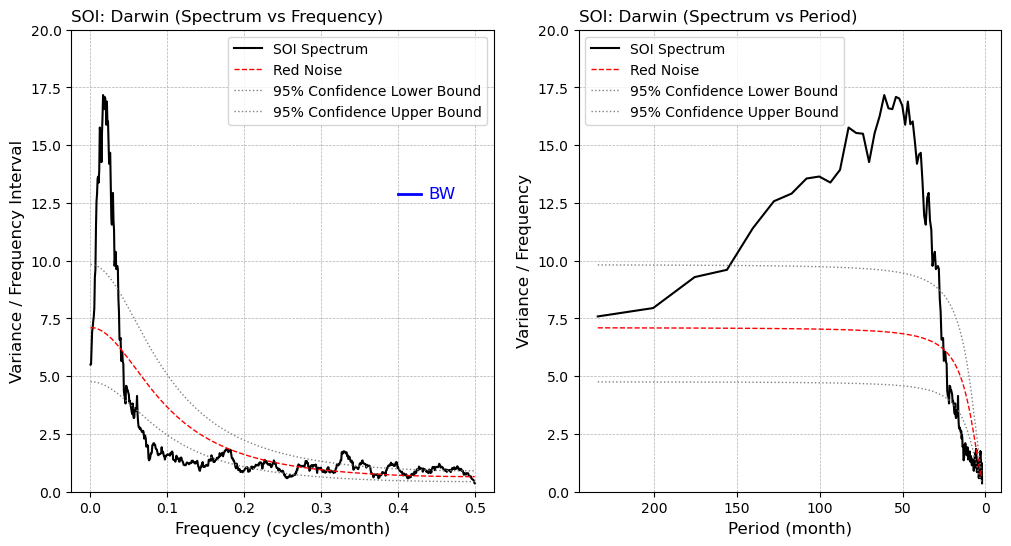
Using the SOI (Southern Oscillation Index) as an example, we will demonstrate the power spectrum calculated by the above functions.
ds = xr.open_dataset("./data/SOI_Darwin.nc")
soi_data = ds['DSOI'].values
# Setting parameters
d = 0 # Detrend option: 0=>remove mean
sm = 21 # Smoothing window: odd number at least 3
pct = 0.10 # Tapering percentage
# Compute spectrum
sdof = specx_anal(soi_data, d, sm, pct)
# Calculate confidence intervals (5% and 95%)
splt = specx_ci(soi_data,sdof, 0.05, 0.95)
Plotting
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(12, 6))
ax=axes.flatten()
# (a) x-axis: frequency
ax[0].plot(sdof['frq'], splt[0,:], label='SOI Spectrum', color='black', lw=1.5)
ax[0].plot(sdof['frq'], splt[1,:], label='Red Noise', color='red', lw=1.0, linestyle='--')
ax[0].plot(sdof['frq'], splt[2,:], label='95% Confidence Lower Bound', color='gray', lw=1.0, linestyle=':')
ax[0].plot(sdof['frq'], splt[3,:], label='95% Confidence Upper Bound', color='gray', lw=1.0, linestyle=':')
ax[0].set_title("SOI: Darwin (Spectrum vs Frequency)", loc='left')
ax[0].set_xlabel("Frequency (cycles/month)", fontsize=12)
ax[0].set_ylabel("Variance / Frequency Interval", fontsize=12)
ax[0].set_ylim(0.0, 20.0)
ax[0].grid(True, which="major", ls="--", linewidth=0.5)
ax[0].legend()
# Plot bandwidth (BW)
bw_x = [0.40, 0.40 + sdof['bw']]
bw_y_val = 0.75 * np.max(sdof['spcx'])
bw_y = [bw_y_val, bw_y_val]
ax[0].plot(bw_x, bw_y, color='blue', lw=2)
ax[0].text(0.41 + sdof['bw'], bw_y_val, "BW", color='blue', va='center', ha='left', fontsize=12)
# (b) x-axis: period
# Convert frequency to period
freqs_nonzero = sdof['frq'][1:]
splt_nonzero = splt[:, 1:]
period = 1 / freqs_nonzero
ip = period <= 240 # Only plot the part where period is less than or equal to 240 months
ax[1].plot(period[ip], splt_nonzero[0, ip], label='SOI Spectrum', color='black', lw=1.5)
ax[1].plot(period[ip], splt_nonzero[1, ip], label='Red Noise', color='red', lw=1.0, linestyle='--')
ax[1].plot(period[ip], splt_nonzero[2, ip], label='95% Confidence Lower Bound', color='gray', lw=1.0, linestyle=':')
ax[1].plot(period[ip], splt_nonzero[3, ip], label='95% Confidence Upper Bound', color='gray', lw=1.0, linestyle=':')
ax[1].set_title("SOI: Darwin (Spectrum vs Period)", loc='left')
ax[1].set_xlabel("Period (month)", fontsize=12)
ax[1].set_ylabel("Variance / Frequency", fontsize=12)
ax[1].set_ylim(0.0, 20.0)
ax[1].grid(True, which="major", ls="--", linewidth=0.5)
ax[1].legend()
ax[1].invert_xaxis()
print(f"Lag-1 autocorrelation (r1): {np.corrcoef(soi_data[:-1], soi_data[1:])[0, 1]:.4f}")
Lag-1 autocorrelation (r1): 0.5348